Load resistor- things you’re never told about it
Load resistor is an output testing device or component which is used as ideal output while designing or testing the electrical circuit.
To figure out what is a load resistor in detail you should know about the term load, where it came from? what is its practical use? Various other forms of it in detail below.
What is a load?
The load is any device that can dissipate a considerable amount of power from the source to give the required output.![]()
So this load can be resistive, capacitive, inductive load or combination of any two.
And the power consumed by them can be in the range of a fraction of Watts to several kiloWatts (uW to kW). The term load is broad in nature so we will try to cover that too in further discussion.
The name load is because it is seen as an added load to the circuit, moreover its characteristic is Load impedance.
Characteristics of the load:
a) It can be passive or active in nature.
b) It can be linear or nonlinear in nature.
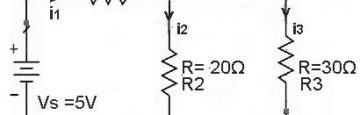
There are three basic types of load impedance (Z):
i) Resistive load [Xr]
iii) Capacitive load [Xc]
iii) Inductive load [Xl]
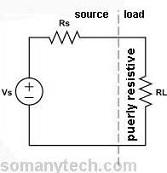
What is a load resistor? -Resistive load:
The load in the circuit which is resistive in nature is called a resistive load or load resistor. The property of a material or a device to resist the flow of electrons through it is called resistivity.
The resistive loads exhibit the property of pure resistivity (there is no reactance or admittance which are the property of capacitor and inductor, XR ≠ 0, XC = 0 and XL = 0 which implies Z = XR )
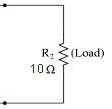
Load resistor symbol:
Load resistor formula:
There is no such particular formula, but if you want to find it then refer to the output resistance of amplifier (in the case of the amplifier only)
- Furthermore, the load resistor is temporary and a mocked output device for designing and testing purposes only.
You will find this ‘TERM‘ in educational curriculum and tutorials but never in real life practical circuits. - In other words, it is simply a resistor that’s been used as a load in various circuits especially which are under test or for experimental purposes.
 Additionally, in practical circuits, there is nothing like a load resistor. This is because output devices with a specific name is used everywhere instead of it.
Additionally, in practical circuits, there is nothing like a load resistor. This is because output devices with a specific name is used everywhere instead of it.
Example of load resistor:
- This can be seen as a speaker is used as an output device in an amplifier circuit in the place of load resistor (RL).
- Besides this LED/ lamp/ light bulbs is used as an indicator in the power converter circuits as an output device instead of (RL).
- Note that the load resistor value can be anything that can handle the output power from the source circuit.

What is a load resistor in circuit?
Below are those things that can be load resistance:
1) Simple resistor
2) Audio speakers
3) LED lights
4) All types of the light indicator
5) Resistive sensors
6) Buzzers
7) The output stage of the radio frequency amplifier or audio frequency amplifier.
8) Antennas
9) High wattage resistor

It also recognized as a discharge load resistor, this type of device has its application in discharging the stored energy in the output capacitor to avoid electric shock or damage of output devices.
USB mini discharge load resistor is commercially available for sale online. Its objective is to discharge USB source circuits so as to avoid accidental electric shock.
Variable Load resistor:
As the name suggests, variable + load + resistor. It is the load that is having variable resistance that can be controlled either manually or by some other means. This image showing a variable load resistor available for the experimental purpose in labs. It comes with various wattage ratings from 5 Watts to 100 Watts and so on. It is also called as a potentiometer.

Generally, a variable load resistor is used to test the effect of Load resistance on the power consumed by the circuit and several other parameters.
ii) Capacitive load:
The load in the circuit which is capacitive in nature can be termed as capacitive load.
The capacitive load can be the combination of capacitor and inductor in which capacitance should be greater than that of inductance (XC > XL). Or the circuit must contain the capacitor only.
iii) Inductive load:
The load connected in the circuit which is inductive can be termed as inductive load.
The inductive load can be the combination of an inductor and capacitor in which inductance should be greater than that of the capacitor (XL > XC). Or the circuit must be purely made of inductors.
FAQ:
What if we don’t use load resistance?
In such case we can not understand the nature of circuit when used load connected and thus circuit analysis is affected.
What if we use a very small load in the power/electrical circuit?
The circuit will deliver a large current and may cause a short circuit which in results can destroy the driver circuit.